Judging by the major indexes, it will take more than the Federal Reserve raising interest rates in the midst of the worst banking mess since the 2008 financial crisis for stock-market investors to lose their cool.
“Investors are broadly assuming that regulators are going to step in and ringfence the sector if need be, and that’s what keeps it from spilling over to the broader market,” said Anastasia Amoroso, chief investment strategist at iCapital, in a phone interview.
There’s also a second reason. Investors see the banking woes forcing the Fed to pause the rate-hike cycle or even begin cutting as early as June, she noted. An end to the yearlong rise in rates will remove a source of pressure on stock-market valuations.
But gains last week, which came amid volatile trading, aren’t sending an all-clear signal, stock-market analysts and investors said.
Banking worries haven’t gone away after the failure of three U.S. institutions earlier this month and UBS Group AG’s
UBS,
UBSG,
agreement to acquire troubled Swiss rival Credit Suisse
CS,
CSGN,
in a merger forced by regulators. Jitters were on display Friday when shares of German financial giant Deutsche Bank
DB,
It’s the fear of runs on U.S. regional banks that still keep investors up at night. Markets might face a test Monday if investors react to Federal Reserve data released after Friday’s closing bell showed deposits at small U.S. banks dropped by a record $119 billion in the weekly period ended Wednesday, March 15, following Silicon Valley Bank’s collapse the preceding Friday.
That sensitivity to deposits was on display last week. U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen was blamed for a late Wednesday selloff that saw the Dow end over 500 points lower after she told lawmakers that her department hadn’t considered or discussed a blanket guarantee for deposits. On Thursday, she told House lawmakers that, “we would be prepared to take additional actions if warranted.”
Deposits are “the epicenter of the crisis of confidence” in U.S. banks, said Kristina Hooper, chief global market strategist at Invesco, in a phone interview. Anything that suggests there won’t be full protection for deposits is bound to worry investors in a charged environment.
See: Is the deposit insurance system broken? 9 things you need to know.
Cascading runs on regional banks would stoke fears of further bank failures and the potential for a full-blown financial crisis, but short of that, pressure on deposits also underline fears the U.S. economy is headed for a credit crunch.
Deposits across banks have been under pressure after the Federal Reserve began aggressively raising interest rates roughly a year ago. Since then, deposits at all domestic banks have fallen by $663 billion, or 3.9%, as money flowed into money-market funds and bonds, noted Paul Ashworth, chief North American economist at Capital Economics, in a Friday note.
“Unless banks are willing to jack up their deposit rates to prevent that flight, they will eventually have to rein in the size of their loan portfolios, with the resulting squeeze on economic activity another reason to expect a recession is coming soon,” he wrote.
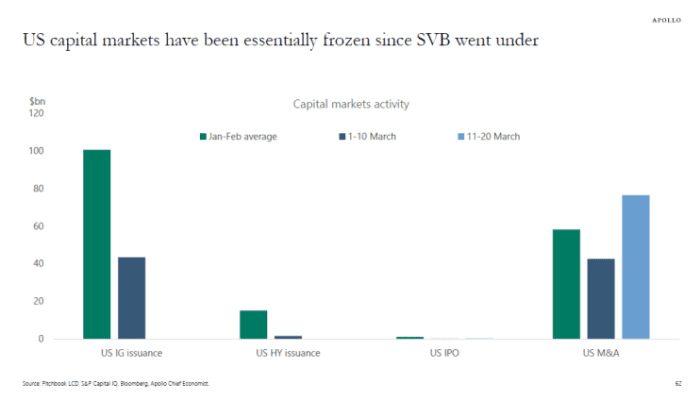
Meanwhile, activity in U.S. capital markets has largely dried up since Silicon Valley Bank’s collapse on March 10, noted Torsten Slok, chief global economist at Apollo Global Management, in a recent note.
Apollo Global Management
There was virtually no investment-grade or high-yield debt issuance and no initial public offerings on U.S. exchanges, while merger and acquisition activity since then represents completed deals that were initiated before SVB’s collapse, he said (see chart above).
“The longer capital markets are closed, and the longer funding spreads for banks remain elevated, the more negative the impact will be on the broader economy,” Slok wrote.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average
DJIA,
rose 1.2% last week, ending a back-to-back run of declines. The S&P 500
SPX,
rose 1.4%, recouping the large-cap benchmark’s March losses to turn flat on the month. The Nasdaq Composite
COMP,
saw a 1.7% weekly rise, leaving the tech-heavy index up 3.2% for the month to date.
Regional bank stocks showed some signs of stability, but have yet to begin a meaningful recovery from steep March losses. The SPDR S&P Regional Banking ETF
KRE,
eked out a 0.2% weekly gain but remains down 29.3% in March. KRE’s plunge has taken it back to levels last seen in November 2020.
First Citizens Bancshares Inc.
FCNCA,
entered a deal to assume all the deposits and loans of the failed Silicon Valley Bridge Bank from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp., the regulator announced on Monday. U.S. stock-index futures pointed higher ahead of Monday’s opening bell, while bank stocks were rising in premarket trade.
Look beneath the surface, and the stock market appears “bifurcated,” said Austin Graff, chief investment officer and founder of Opal Capital.
Much of the resilience in the broader market is attributable to gains for megacap technology stocks, which have enjoyed a flight-to-safety role, he said in a phone interview.
The megacap tech-heavy Nasdaq-100
NDX,
was up 6% in March through Friday’s close, according to FactSet, while regional bank shares dragged on the small-cap Russell 2000
RUT,
down 8.5% over the same stretch.
For investors, “the expectation should be for continued volatility because we do have less money flowing through the economy,” Graff said. There’s more pain to be felt in highly levered parts of the economy that weren’t prepared for the speed and scope of the Fed’s aggressive rate increases, including areas like commercial real estate that are also struggling with the work-from-home phenomenon.
Graff has been buying companies in traditionally defensive sectors, such as utilities, consumer staples and healthcare, that are expected to be resilient during economic downturns.
Invesco’s Hooper said it makes sense for tactical allocators to position defensively right now.
“But I think there has to be a recognition that if the banking issues that we’re seeing do appear to be resolved and the Fed has paused, we are likely to see a market regime shift…to a more risk-on environment,” she said. That would favor “overweight” positions in equities, including cyclical and small-cap stocks as well as moving further out on the risk spectrum on fixed income.
The problem, she said, is the well-known difficulty in timing the market.
Amoroso at iCapital said a “barbell” approach would allow investors to “get paid while they wait” by taking advantage of decent yields in cash, short- and long-term Treasurys, corporate bonds and private credit, while at the same time using dollar-cost averaging to take advantage of opportunities where valuations have been reset to the downside.
“It doesn’t feel great for investors, but the reality is that we’re likely trapped in a narrow range for the S&P for a while,” Amoroso said, “until either growth breaks to the downside or inflation breaks to the downside.”
